Historia Battles WW2 CFEL Mac OS
So I just fought with Mac OS Classic and an Ethernet card(s) for months. I thought it wasn’t working because it wouldn’t pull a dhcp address. I plug it in, I get a link light on the NIC and switch. While watching the IP address field in the TCP/IP control panel, it never populates. Download Tank Battles 1.0.0 for Mac from our website for free. This software for Mac OS X was originally produced by Gameloft. This Mac download was scanned by our antivirus and was rated as clean. The software lies within Games, more precisely Action. Call of Duty Warzone Mac OS X – TOP macOS Battle Royale – After PUBG and Apex Legends, now it’s time for Call of Duty Warzone to reach the top. This game is the second battle royale title in the COD series. It doesn’t require the Call of Duty: Modern Warfare game in order to enjoy its full features set. The years after WWII saw rapidly increasing tensions between the US and USSR, as each walked a fine line between expanding their power while avoiding nuclear war. By the early 1960's, the US had clearly pulled ahead in strategic capabilities with a much superior long-range ICBM force. The 'Battles of the Ancient World' game system is a tactical simulation of some of the greatest and most important battles from ancient history from 1457 B.C. Each of the 18 scenarios available features one of these great battles and players may play as either side. Each unit in the g.
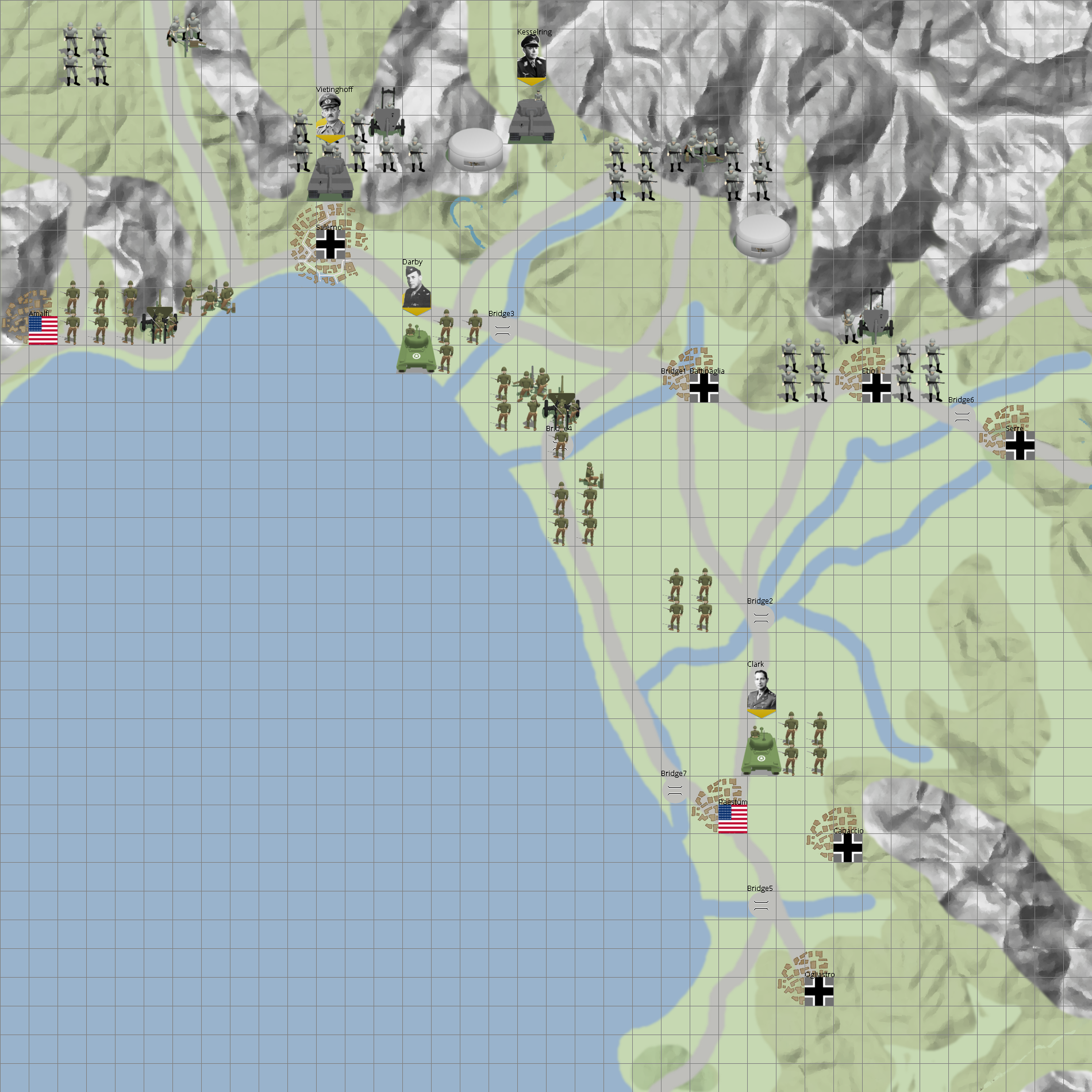
This is a list of all battles involving the United States during World War II.
| Name | Start Date | End Date | Location | Campaign | U.S. Casualties | Result | Opposing Force | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battle of the Atlantic | September 13, 1941 | May 8, 1945 | Atlantic Ocean, North Sea, Irish Sea, Labrador Sea, Gulf of St. Lawrence, Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, Outer Banks, Arctic Ocean | Around 18,000 sailors and merchant seamen killed [1][2] | Allied victory | Germany, Japan (Possibly), Currently unknown |
| |
| Operation Torch | November 8, 1942 | November 10, 1942 | Morocco and Algeria | North African Campaign | 1,200 (479 killed, 720 wounded)[3] | Allied victory | Vichy France Germany |
|
| Battle of the Kasserine Pass | February 19, 1943 | February 25, 1943 | Kasserine Pass, Tunisia | Tunisia Campaign | 6,500 (1,000+ killed);[3][4] or, 9,195 (2,572 killed, 5,946 wounded and 1,012 captured or missing)[5] | Axis tactical victory | Germany and Italy |
|
| Battle of El Guettar | March 23, 1943 | April 7, 1943 | El Guettar, Tunisia | Tunisia Campaign | ~5,000[6] | Indecisive | Germany and Italy | |
| Battle of Gela | July 10, 1943 | July 12, 1943 | Gela, Sicily | Italian Campaign | 2,300, 1 destroyer sunk[3] | Allied victory | Germany and Italy |
|
| Battle of Salerno | September 9, 1943 | September 16, 1943 | Salerno, Italy | Italian Campaign | 4,870[7] | Allied victory | Germany and Italy |
|
| Battle of Monte Cassino | January 17, 1944 | May 18, 1944 | Monte Cassino, Italy | Italian Campaign | 100,000+ (Total allied casualties)[3] | Allied victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Anzio | January 22, 1944 | June 5, 1944 | Anzio and Nettuno, Italy | Italian Campaign | 23,173 (5,538 killed, 15,558 wounded and 2,947 captured or missing)[8] | Allied victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Normandy | June 6, 1944 | July 24, 1944 | Normandy, France | Operation Overlord | 63,360 (16,293 killed, 43,221 wounded and 6,180 captured or missing)[8] | Allied victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Graignes | June 10, 1944 | June 12, 1944 | Graignes, France | Operation Overlord | 32 (17 executed)[3] | American victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Carentan | June 10, 1944 | June 14, 1944 | Carentan, France | Operation Overlord | American victory | Germany |
| |
| Battle for Brest | August 7, 1944 | September 19, 1944 | Brittany, France | Operation Overlord | ~4,000[9] | Allied victory | Germany |
|
| Operation Dragoon | August 15, 1944 | September 14, 1944 | Southern France | Operation Overlord | 15,574 (7,301 killed, 5,804 wounded, 3,098 captured or missing)[5] | Allied victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Nancy | September 5, 1944 | September 15, 1944 | Nancy, France | Siegfried Line campaign | 2,851+[3] | American victory | Germany |
|
| Operation Market Garden | September 17, 1944 | September 25, 1944 | The Netherlands | Siegfried Line campaign | 3,974[3] | Allied operational failure | Germany |
|
| Battle of Hürtgen Forest | September 19, 1944 | February 10, 1945 | Hurtgen Forest, German-Belgian border | Siegfried Line campaign | 33,000[3] | German defensive victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Metz | September 27, 1944 | December 13, 1944 | Metz, France | Siegfried Line campaign | 2,851+[3] | American tactical victory, German strategic victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Aachen | October 2, 1944 | October 21, 1944 | Aachen, Germany | Siegfried Line campaign | 5,000[3] | American victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of the Bulge | December 16, 1944 | January 25, 1945 | The Ardennes, Belgium, Luxembourg, and Germany | Siegfried Line campaign | 89,500 (19,000 killed, 47,500 wounded, 23,000 missing)[10] | Allied victory | Germany |
|
| Operation Nordwind | January 1, 1945 | January 25, 1945 | Alsace and Lorraine, France | Siegfried Line campaign | 12,000 (3,000 killed, 9,000 wounded or missing)[11] | German operational failure | Germany |
|
| Colmar Pocket | January 20, 1945 | February 9, 1945 | Alsace, France | Siegfried Line campaign | 8,000[3] | Allied victory | Germany |
|
| Ruhr Pocket | March 7, 1945 | April 21, 1945 | Ruhr Area, Germany | Western Allied invasion of Germany | Allied victory | Germany |
| |
| Operation Varsity | March 24, 1945 | Wesel, Germany | Western Allied invasion of Germany | 2,700[3] | Allied victory | Germany |
| |
| Battle of Frankfurt | March 26, 1945 | March 29, 1945 | Frankfurt, Germany | Western Allied invasion of Germany | unknown[3] | American victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Paderborn | March 30, 1945 | March 31, 1945 | Paderborn, Germany | Western Allied invasion of Germany | American victory | Germany |
| |
| Battle of Kassel | April 1, 1945 | April 4, 1945 | Kassel, Germany | Western Allied invasion of Germany | Unknown[3] | American victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Heilbronn | April 4, 1945 | April 12, 1945 | Heilbronn, Germany | Western Allied invasion of Germany | 422 (60 killed, 250 wounded, 112 missing)[3] | American victory | Germany |
|
| Battle of Nuremberg | April 16, 1945 | April 20, 1945 | Nuremberg, Germany | Western Allied invasion of Germany | American victory | Germany |
| |
| Spring 1945 offensive in Italy | April 6, 1945 | May 2, 1945 | Northern Italy | Italian Campaign | 16,258 (1,288 killed, 15,453 wounded and 93 missing)[3] | Allied victory | Germany |
|
| Attack on Pearl Harbor | December 7, 1941 | Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, United States | 3,592 (2,345 killed and 1,247 wounded)[3] | Japanese tactical victory | Japan |
| ||
| Battle of Wake Island | December 8, 1941 | December 23, 1941 | Wake Island | 627 (130 killed, 49 wounded and 448 captured)[3] | Japanese victory | Japan |
| |
| Battle of Bataan | January 7, 1942 | April 9, 1942 | Bataan Peninsula, Philippines | Philippines campaign (1941–1942) | 15,000 captured and interned[3] | Japanese victory | Japan |
|
| Doolittle Raid | April 18, 1942 | Tokyo and other Japanese cities | 3 killed and 8 later died in captivity/executed | US propaganda victory | Japan |
| ||
| Battle of the Coral Sea | May 4, 1942 | May 8, 1942 | Coral Sea, between Australia, New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands | New Guinea campaign | 656 killed | Japanese tactical victory, Allied strategic victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Milne Bay | August 25, 1942 | September 7, 1942 | Milne Bay, Papua New Guinea | New Guinea campaign | 14 killed[3] | Allied victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Wau | 29 January 1943 | February 4, 1943 | Wau, Papua New Guinea | New Guinea campaign | Allied victory | Japan |
| |
| Battle of Wakde | 18 May 1944 | 21, May 1944 | Wakde, Indonesia | New Guinea campaign | 147 (40 killed, 107 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Biak | 27 May 1944 | August 17, 1944 | Biak, Indonesia | New Guinea campaign | Allied victory | Japan |
| |
| Battle of Driniumor River | July 10, 1944 | August 25, 1944 | Near Aitape, Papau New Guinea | New Guinea campaign | 3,000 (440 killed and 2,560 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Sansapor | July 30, 1944 | August 31, 1944 | Bird's Head Peninsula, Indonesia | New Guinea campaign | 49 (15 killed and 35 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan | |
| Battle of Midway | June 3, 1942 | June 7, 1942 | Near Midway Atoll | 307 killed[12] | American victory | Japan |
| |
| Battle of Guadalcanal | August 7, 1942 | February 9, 1943 | Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands | Solomon Islands campaign | ~6,000 (1,600 killed, 4,400 wounded and missing they were never found)[13] | Allied victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands | October 25, 1942 | October 27, 1942 | Santa Cruz Islands, Solomon Islands | Solomon Islands campaign | 266 killed[3] | Japanese tactical victory, American strategic victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Tarawa | November 20, 1943 | November 23, 1943 | Betio, Tarawa Atoll | Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign | 3,296 (1,000 killed and 2,296 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Makin | November 20, 1943 | November 24, 1943 | Makin Atoll, Gilbert Islands | Gilber and Marshall Islands campaign | 948 (763 killed and 185 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan | |
| Battle of Kwajalein | January 31, 1944 | February 3, 1944 | Kwajalein Atoll, Marshall Islands | Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign | 1,964 (372 killed and 1,592 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Eniwetok | February 17, 1944 | February 23, 1944 | Enewetok Atoll, Marshall Islands | Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign | 1,269 (313 killed, 879 wounded, 77 missing)[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Saipan | June 15, 1944 | July 9, 1944 | Saipan, Mariana Islands | Mariana and Palau Islands campaign | 13,313 (2,949 killed and 10,364 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of the Philippine Sea | June 19, 1944 | June 20, 1944 | Philippine Sea | Mariana and Palau Islands campaign | 109 killed[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Guam | July 21, 1944 | August 8, 1944 | Guam, Mariana Islands | Mariana and Palau Islands campaign | 7,800 (1,747 killed and 6,053 wounded)[3] | Allied victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Tinian | July 24, 1944 | August 1, 1944 | Tinian, Mariana Islands | Mariana and Palau Islands campaign | 1,919 (326 killed and 1,593 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Peleliu | September 15, 1944 | November 27, 1944 | Peleliu, Palau Islands | Mariana and Palau Islands campaign | 9,804 (1,794 killed and 8,010 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Angaur | September 17, 1944 | September 30, 1944 | Angaur, Palau Islands | Mariana and Palau Islands campaign | 260 killed[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Leyte Gulf | October 23, 1944 | October 26, 1944 | Leyte Gulf, Philippines | Philippines campaign (1944–45) | ~1,500 killed[3] | Allied victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Luzon | January 9, 1945 | August 15, 1945 | Luzon, Philippines | Philippines campaign (1944–45) | ~37,870 (8,310 killed and 29,560 wounded)[3] | Allied victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Manila | February 3, 1945 | March 3, 1945 | Manila, Philippines | Philippines campaign (1944–45) | 6,575 (1,010 killed and 5,565 wounded)[3] | Allied victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Bessang Pass | June 1, 1945 | June 15, 1945 | Ilocos Sur, Philippines | Philippines campaign (1944–45) | 339 (119 killed and 220 wounded)[3] | Allied victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Iwo Jima | February 19, 1945 | March 26, 1945 | Iwo Jima, Japan | Volcano and Ryukyu Islands campaign | 26,038 (6,821 killed and 19,217 wounded)[3] | American victory | Japan |
|
| Battle of Okinawa | April 1, 1945 | June 22, 1945 | Okinawa, Japan | Volcano and Ryukyu Islands campaign | 51,429 (12,513 killed and 38,916 wounded)[3] | Allied victory | Japan |
|
References[edit]
- ^http://www.usmm.org/casualty.html U.S. Merchant Marine Casualties during World War II
- ^http://www.history.navy.mil/library/online/ww2_statistics.htm#active_enl US Navy Personnel in World War II: Service and Casualty Statistics[dead link]
- ^ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzaaabacadaeafagahaiajakalamanReferences in the article
- ^http://www.history.com/this-day-in-history.do?action=Article&id=6712Archived 2010-02-13 at the Wayback Machine History.com
- ^ abhttp://cgsc.cdmhost.com/cdm4/document.php?CISOROOT=/p4013coll8&CISOPTR=130&REC=2Army Battle Casualties and Nonbattle deaths in World War II p.93
- ^Zaloga, S, (2005), Kasserine Pass 1943: Rommel's Last Victory. Osprey Publishing
- ^tduvall. 'Salerno: Conclusion'. www.history.army.mil.
- ^ abhttp://cgsc.cdmhost.com/cdm4/document.php?CISOROOT=/p4013coll8&CISOPTR=130&REC=2Army Battle Casualties and Nonbattle deaths in World War II p.92
- ^'Archived copy'. Archived from the original on 2008-07-04. Retrieved 2008-08-30.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^http://www.defense.gov/news/newsarticle.aspx?id=24591 United States Department of Defense
- ^Smith and Clark, Riviera To The Rhine, p. 527.
- ^http://ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USN/USN-CN-Midway/USN-CN-Midway-13.html#our The Battle of Midway
- ^Shaw, A, (2002), World War II: Day by Day. Grange Books, p. 105
- StoreBrowse Genres
- Specials
- Support
- 0
- Your cart is empty!
- Buy with confidence. All products on MacGameStore are authorized for sale by publishers. No gray-market worries here!
| Would you like to view prices in estimated EUR? (actual charges are made in USD) | Yes | Historia Battles Ww2 Cfel Mac Os IsoRegion restrictionsThis game has world-wide activation. No known region restrictions in effect.
DescriptionStrategy & Tactics: Wargame Collection is a set of three historical turn-based strategies, in which you are going to take command of the armies in the greatest Medieval wars as well as take control of countries and nations during World War II. Strategy & Tactics: WW II Become a general of one of the most important WW II battles! Take command of the German, Soviet or Allied army and lead them to victory in three challenging story-based campaigns. Single player scenario-based battles will satisfy those who love huge maps taking several hours to complete as well as quick skirmish lovers. Medieval Wars: Strategy & Tactics You will send the armies of England, France, and Crusader forces in three campaigns, trying to defeat your enemies in the major European wars and battles in the IX-XV centuries. With the scenario-based maps you will take part in battles for the Rus', stop the Saracens under the banners of Charles the Great and spark the Hussite uprising. WW2: Sandbox. Strategy&Tactics Win the victory in World War II for one of the 28 countries at your choice. You can keep the political alliances that existed in reality and, for instance, lead the USSR and crush Germany together with the Western allies, or you can disable the alliances and celebrate your victory on the ruins of London. The generator of random events, such as guerilla movements, landing operations, voluntary recalls, etc., will add to the replaying possibilities of each game, making it your own unique part of history. Strategy & tactics: ww ii:
Medieval wars: strategy & tactics:
Ww2: sandbox. strategy&tactics:Historia Battles Ww2 Cfel Mac Os 11
Requirements
Turn On Javascript  Be the first to submit a review! Sign In to submit a review. More By HeroCraft Ltd
|